 Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more
Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver. Without treatment, the virus can lead to complications, such as scarring and long term liver damage, which in turn can become chronic, liver failure and liver cancer. Often, people who have chronic HCV do not experience symptoms until they have developed extensive liver damage.
Clinical Features of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C if contracted by an individual might be difficult to notice, showing no signs or little symptoms, yet, it is important to know the stages of hepatitis C due to its symptoms.
Stages of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
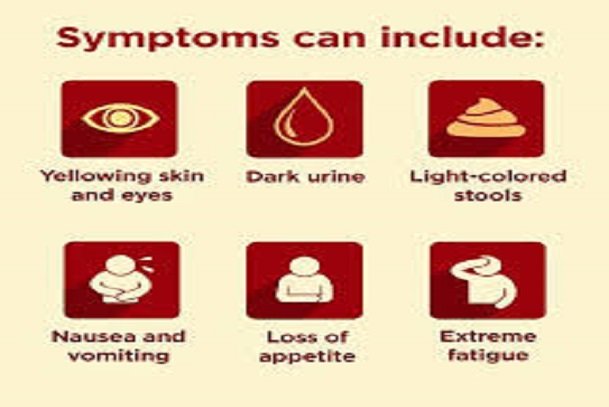
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Early Symptoms of Hepatitis C
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 80 percent or more of individuals with acute hepatitis C won’t experience hepatitis C symptoms. But some individuals experience symptoms not long after being infected. These symptoms can either be mild or severe and they include:
After the hepatitis C virus enters the human bloodstream, between 2 weeks and 6 months, the following symptoms begins to show up
Chronic (Advanced) Hepatitis C
After a while, individuals with chronic HCV infection may develop signs of liver inflammation i.e. swellings which may suggests that an infection may be present. These infected individuals may become easily fatigued or complain of nonspecific symptoms.
Symptoms of Advanced Hepatitis C
The following symptoms could also be felt along with acute hepatitis C symptoms:
Complications of Hepatitis C
Most people who do not receive treatment for acute HCV go on to develop chronic HCV. A person with chronic HCV may experience the following complications.
Liver Disease
Liver disease is a multistage process that begins with inflammation of the liver and can take a long time to progress. Chronic inflammation caused hepatitis C damages the liver and causes a buildup of scar tissue within the organ, which is called fibrosis.
As the scar tissue grows, it replaces healthy liver tissue, and this result in the liver becoming increasingly less able to function as it ought to.
Over time, fibrosis may lead to more extensive and severe liver scarring, called cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver. Over time, hard scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue in a process called fibrosis. The scar tissue can also block blood flow through the liver.
Whenever a liver develops too much scar tissue, the liver won’t function properly. If cirrhosis isn’t managed, it can lead to liver failure.
Liver Failure
The moment cirrhosis is managed, an individual develops liver failure, thus their liver losses its ability to function properly. Liver failure is a life threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. It symptoms includes:
When liver failure occurs as a result of cirrhosis, doctors sometimes refer to it as end stage liver disease (ESLD). In some cases, it can take months, years, or even decades for a person to develop ESLD. People with chronic liver disease may require a liver transplant.
As liver failure progresses, a person may notice the following symptoms:
Liver Cancer
Chronic hepatitis C infection increases a person’s risk of developing liver cancer. Even after HCV treatment, a person who has severe liver damage remains at increased risk of developing liver cancer.
[Next Article on Hepatitis C: Management of Hepatitis C]