Lung cancer is the world third most diagnosed cancer among both genders (male or female). It is a cancer that starts from the lungs and often occurs among people who smokes. Nevertheless, there is a certain percentage of this type of cancer found in people who don’t smoke at all. Without proper treatment or preventive measures taken, it can become chronic; thereby leading to the cause of death among the individual.
Although, it doesn’t show early symptoms unlike breast cancer or prostate cancer among women and men respectively, yet it can be avoided if certain preventive measures are kept in place.
Clinical Features of Lung Cancer
Due to its relativeness of being asymptomatic (i.e. showing no symptoms except it gets to a critical stage) in individuals, lung cancer has some certain clinical features that showcases during certain stages as its danger loom.
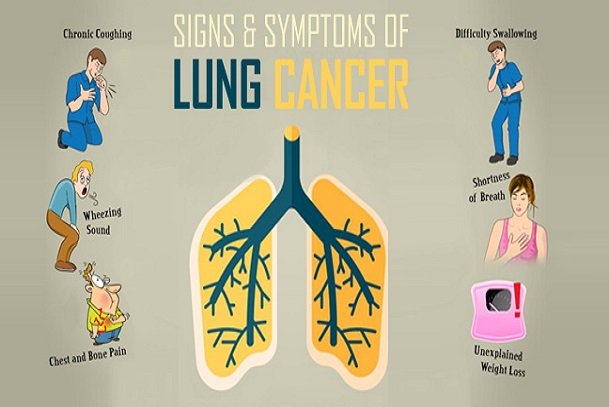
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Most lung cancers don’t cause any form of symptoms until they might have spread; yet some individual do have early lung cancer symptoms, making it easy to be diagnosed at an earlier stage when treatment is more likely to be effective.
Early Symptoms of Lung Cancer may include:
- A cough that keeps lingering or gets worse
- Coughing up blood or phlegm (rust coloured sputum)
- Shortness of breath
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Chest pain that worsens as one takes a deep breath, cough or laughs
- Unexplained weight loss
- Feeling weak or tired (fatigue)
- Wheeziness
- Recurrent respiratory infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia that keeps going back and forth
Strongly suspect lung cancer if the above symptoms occur in a middle aged elderly person who smokes. Additional symptoms begin to emanate from the body the moment the cancer spreads and form new symptoms. These symptoms depend on the various part of organ it might have spread to. For example, if in the:
- Lymph Nodes: There are lumps building up, particularly around the collarbone and neck.
- Bones: Consistent bone pain especially in the back, ribs or hips.
- Liver: There is a yellowing or the skin and eyes (jaundice).
- Brain or Spine: Constant headache, dizziness, numbness in the arms or legs and body balance issues.
Complications of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer can cause complications in the human body, and they include:
- Hemoptysis: Lung cancer can cause bleeding in the airway, which causes hemoptysis (coughing up blood). This bleeding can become severe and sometimes need treatments to control such bleeding.
- Shortness of Breath: Just like its symptoms, lung cancer complications can cause shortness of breath. Experiencing shortness of breath can be found in people with lung cancer once the cancer grows and block major airways. It can cause fluid to accumulate around the lungs, making it very hard for the affected lung to expand fully once an individual breathes.
- Pleural Effusion: Lung cancer can cause certain fluid to accumulate in most spaces that surrounds the affected lung in the pleural space. Causing shortness of breath, treatments are available to drain the fluid and reduce the reoccurrence of pleural effusion.
- Pain: Once lung cancer gets to the advanced stage or spread to other parts of the body such as the bone, it can cause pain and create a bad experience to the individual.
- Metastasis Lung Cancer: Lung cancer often spreads to other organs of the body, such as the brain and bones. And this causes pain, nausea, headaches or other signs and symptoms depending on what organ is affected. The moment it spreads beyond the lungs, it becomes non – curable.
[Next on Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment]
 Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more
Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more