Skin cancer is a form of cancer that affects the skin, and like other cancers; they are abnormal growth that becomes dangerous on the human skin.
Except in quite rare cases, skin cancer occurs when there are errors or mutations in the DNA of the skin cells induced from the ultraviolet light affecting the cells of the epidermis; causing these cells to grow out of control and thus forming a mass of cancer cells.
The skin cancer always begins its circulation from the top layer of the skins i.e. the epidermis. The epidermis is a thin layer that acts a protective cover for the skin. And it contains three main types of cells:
- Squamous Cells: These cell lies below the outer surface of the skin and acts as the skin’s inner lining.
- Basal Cells: These cells are responsible for the production of new skin cells when the old skins fades away; and they are a little beneath the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: These cells are responsible for the production of the melanin. The melanin is a form of pigment that gives the skin its natural colour (it’s located in the lower part of the epidermis). The melanocytes produce more melanin so as to help protect the skin from getting sun burned.
Whenever the DNA in the skin cells are damaged, it is usually a result of the excess ultraviolet lighting found in the sunlight or/and the lights used in tanning, yet it doesn’t mean that skin cancers can develop through ordinarily being exposed to sunlight. This means that there are other risk factors that may contribute to one’s risk of getting skin cancer.
Risk Factors of Skin Cancer
As it well known that the ultraviolet radiation from the sun causes skin cancer, that doesn’t imply that one can get skin cancer by ordinarily walking or staying under the sunlight; there are other factors that contribute to having skin cancer such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens the immune system.
- Having a History of Sunburns: The moment an individual has had one or more blistering sunburns as a child, and as a teenager; the risk of developing skin cancer as an adult may likely increase. Also sunburns as an adult is a risk factor.
- Excess Sun Exposure: When an individual is excessively exposed to the sun may develop skin cancer, especially when not properly protected by clothing or sunshades. Exposure to tanning lamps could put one at a risk too. Tanning is the skin’s injury to excessive ultraviolet radiation.
- Having Fair Skin: Different people different natural skin colour, yet anyone irrespective of their skin colour can develop skin cancer. However, having a less pigment (melanin) in the skin put the skin at risk due to the damages of the ultraviolet radiation from the sun. When an individual gets sunburn easily, e.g. blonde or red – haired, Caucasians, African albinos; they are all potentially at greater risk of skin cancer.
- Family History of Skin Cancer: Although skin cancer is not a hereditary form of cancer, but when there is a history of skin cancer in the family especially from one’s parent or siblings, there is an increased risk of skin cancer.
- Personal History of Skin Cancer: If there is a personal history of developed skin cancer (especially non melanoma), there is an increased of developing skin cancer once again.
- Climates: People who live under sunny and warm climates are usually exposed to more sunlight than those who lives in much colder and less sunny climates. Living under these climate conditions (especially in tropical regions) may increase the risk of developing skin cancer due to more ultraviolet radiation.
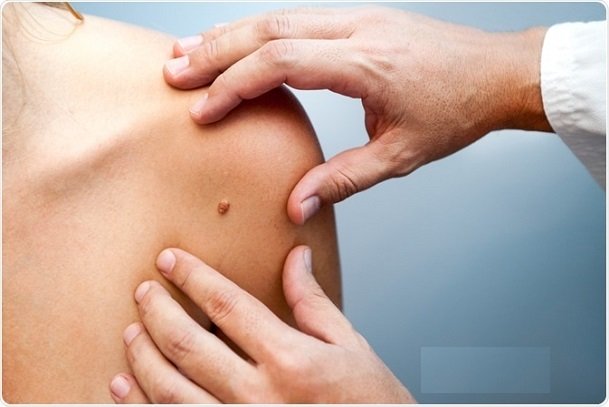
- Moles: People who have many moles or abnormal moles (dysplastic nevi) are at an increased risk of developing skin cancer. These abnormal moles are more likely to become cancerous.
- Weak Immune System: People with weakened immune system have a higher risk of developing skin cancer. This includes individuals living with HIV/AIDS or people taking immunosuppressant drugs after getting an organ transplant.
- Been Exposed to Radiation: Individuals who might have had a radiation treatment for skin conditions (e.g. acne and eczema) have a risk of developing skin cancer, most especially basal cell carcinoma
- Precancerous Skin Lesions: Having skin lesions known as actinic keratosis can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. These precancerous skin growths typically appear as rough, scaly patches that range in color from brown to dark pink. They're most common on the face, head and hands of fair-skinned people whose skin has been sun damaged.
- Exposed to Other Substances: Constant exposure to certain toxic environmental substances such as lead, mercury, arsenic, asbestos, pesticide chemicals etc., may increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
[Next on Skin Cancer: How Skin Cancer Manifest]
 Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more
Wash your hands regularly and wear a face mask.
Learn more